Working with applications
Lentiq provides a series of essential open source applications or application clusters that can be deployed as managed services in a data pool. All our applications are resilient and will survive node or container failures.
- Managed by Lentiq
- Low provision and startup time
- Preconfigured for secure access to the data in the data pool
- Support multiple instances or versions of the same application within the same project
- Scalable both horizontally and vertically
Deploying applications
Deploying applications and clusters can be done either via the UI or via the API. The applications will consume resources from the project's allocation from the data pool.
Scaling applications
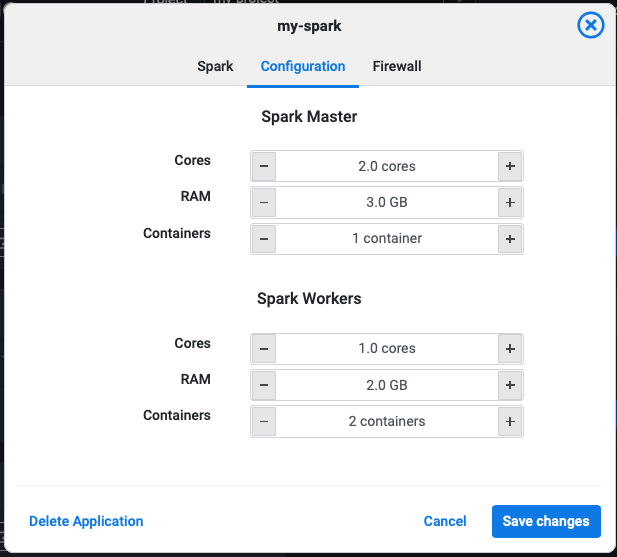
Application clusters can typically be scaled horizontally and vertically, depending on each applications’ architecture. For example Spark has master containers and worker containers and are scalable independently.
Application networking
There two ways to access applications in Lentiq:
- Externally: This is done via services (load balancers) and through the application's firewall.
- Internally: Applications can talk directly to each other via the internal network and discover each other using the internal DNS records such as: my-project-my-spark-bdl-spark-master.my-project.svc.cluster.local
Supported Applications
Jupyter
This is the de-facto notebook technology for data scientists and it is integrated with the Spark engine as well as the standard NumPy, Ray, Dash, Seaborn, Scikit-learn, SciPy, matplotlib and other tools for the Python and Scala programming languages.
Apache Spark
A pay-per-use, fully managed, large scale, in-memory data processing service capable of machine learning and graph processing that leverages Apache Spark. In each project, one can provision multiple, independent, smaller clusters for separate jobs, to simplify management in multi-tenant environments.
SparkSQL
SparkSQL is a service that allows industry standard JDBC and ODBC connectivity for business intelligence tools to data coming from a variety of sources and Spark programs. It can allow users to seamlessly connect with Tableau, Looker, QlikView, Zoomdata or PowerBI.
Kafka
Is a fast, scalable, queuing system, designed as an intermediate layer between producers and consumers of data. It can be used to bring data into Lentiq by connecting it via Spark Streaming jobs.
SFTPProxy
SFTPProxy is a service that allows you to easily import high-volume data into a project within the data lake.
Streamsets
Is an open source data ingestion and transformation engine that streamlines data integration tasks.
